In today’s fast-growing food environment, many people rely on quick, cheap, and highly processed foods. While convenient, these foods often contain trans fats—one of the most harmful types of fats linked to rising rates of chronic diseases worldwide. Understanding what trans fats are, where they are found, and how healthier fat choices can protect your well-being is essential for every household and community.
What Are Trans Fats?
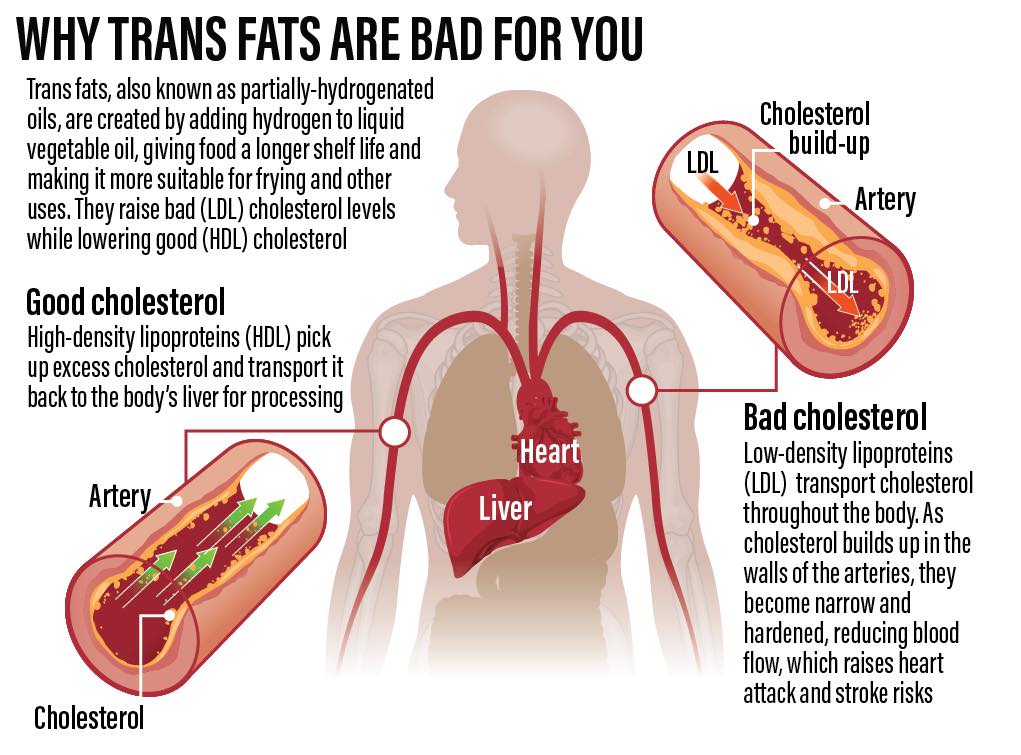
Trans fats are a type of unhealthy fat created through a process called hydrogenation, which turns liquid oils into solid fats to improve shelf life and texture. Although some trans fats occur naturally in small amounts in animal foods, the most dangerous form is industrial trans fat, commonly found in processed and fried foods.
Research shows that trans fats:
- Increase bad cholesterol (LDL)
- Lower good cholesterol (HDL)
- Promote inflammation
- Damage blood vessels
- Increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and obesity
Because of these harmful effects, the World Health Organization has called for the global elimination of industrial trans fats.
Common Foods That Contain Trans Fats

Trans fats often hide in everyday foods, especially those that are processed or fried. Some major sources include:
- Packaged snacks: biscuits, cookies, crackers
- Fried foods: doughnuts, chips, fried chicken
- Margarines and shortening
- Some bakery products: cakes, pastries, pies
- Fast foods
- Microwave popcorn
- Non-dairy creamers
Always check the nutrition label. If you see “partially hydrogenated oils”, the product contains trans fats.
The Link Between Trans Fats and Chronic Diseases
A diet high in trans fats significantly increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as:
1. Cardiovascular Diseases
Trans fats cause plaque buildup in arteries, raising the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
They interfere with insulin function, increasing insulin resistance.
3. Obesity
Trans fats encourage fat accumulation around the abdomen, a major risk factor for metabolic diseases.
4. Inflammation
They elevate inflammatory markers in the body, which can trigger long-term health issues.
These chronic diseases are preventable through healthier dietary habits—and one of the simplest steps is choosing better fats.
Healthy Fat Choices: What to Eat Instead
Not all fats are harmful. In fact, your body needs healthy fats to function well. Replacing trans fats with unsaturated fats can drastically improve your health.
Healthy Fat Sources Include:
1. Monounsaturated Fats
- Olive oil
- Avocado
- Nuts (almonds, cashews, peanuts)
- Sesame and canola oil
2. Polyunsaturated Fats
- Sunflower oil
- Soybean oil
- Fish (sardines, salmon, mackerel)
- Walnuts
- Chia and flax seeds
These fats help reduce cholesterol levels, support heart health, improve brain function, and lower inflammation.

Practical Tips to Reduce Trans Fat Intake
- Choose foods labeled “trans fat free”
- Cook with healthy oils instead of solid fats
- Reduce consumption of fast foods and deep-fried snacks
- Prepare more meals at home using whole, fresh ingredients
- Read labels carefully—avoid products with “partially hydrogenated oils”
- Replace margarine with healthier spreads or natural options
Conclusion: Protecting Community Health Through Better Fat Choices
Trans fats contribute significantly to the growing burden of chronic diseases. However, this trend can be reversed. By choosing healthier fats and reducing consumption of processed and fried foods, families and communities can prevent heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and other long-term health problems.
At HRDO, we continue to advocate for better nutrition, public health awareness, and stronger community education to ensure healthier, happier lives for all.